Introduction: Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease (GALD) is a rare disease characterized by subacute fetal liver injury and often accompanied by hepatic and extrahepatic iron deposition. Findings include hypoglycemia, coagulopathy, hypoalbuminemia, elevated serum ferritin, elevated alpha-fetoprotein, and ascites. Extrahepatic hemosiderin deposition is often seen in salivary glands. Previously, the mortality rate was close to 80% with all patients needing liver transplantation. With maternal IVIG treatment and changes in neonatal treatment, there is now less than 20% mortality with infrequent need for liver transplantation. Diagnosis of GALD is typically done on a postmortem analysis.
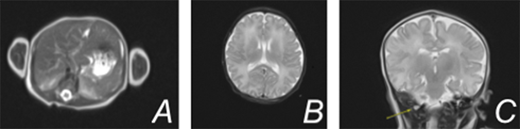
Case Description: A term female infant was born via scheduled c-section to a 32 year old G2P1000 mother who had been receiving weekly IVIG during this pregnancy due to the death of her first child at 4 days of life. Autopsy of that female baby demonstrated extensive neuropathological changes, liver steatosis, iron depletion, and ascites, consistent with GALD. Following delivery of our current patient, there was an elevated alpha-fetoprotein (greater than 80,000), decreased fibrinogen, and coagulopathy with peak international normalized ratio of 1.6. The patient received fresh frozen plasma and IVIG on day of life 1 with improvement of these levels. Complete blood count, liver function tests, and ammonia were within normal limits. An MRI of the liver demonstrated normal size, morphology, and normal iron levels based on T2 relaxometry. A buccal biopsy did not demonstrate extrahepatic iron deposition. MRI of the brain showed significant stenosis of the right transverse and sigmoid sinus relating to dural venous sinus thrombosis. There was no evidence of parenchymal infarction and no evidence of iron deposition. At this time, enoxaparin was initiated. The patient was discharged home on day of life nine on enoxaparin therapy.
Discussion: There are few reported cases of patients with GALD, especially after maternal IVIG treatment. This case report exemplifies the effect of antenatal IVIG infusions during subsequent pregnancies in women with a history of GALD in prior children. This effect is protective, evidenced by lack of liver injury noted in this patient. This supports the use of immunotherapy during pregnancy to prevent recurrence of alloimmune injury.
References:
1. Is exchange transfusion a possible treatment for neonatal hemochromatosis?
Giuseppina Timpani-Francesca Foti-Antonino Nicolò-Pier Nicotina-Emanuele Nicastro-Raffaele Iorio - Journal of Hepatology - 2007
2. Medical and surgical treatment of neonatal hemochromatosis: Single center experience-Thomas Heffron-Todd Pillen-David Welch-Massimo Asolati-Gregory Smallwood-Phil Hagedorn-Carlos Fasola-David Solis-John Rodrigues-Jill Depaolo-James Spivey-Enrique Martinez-Stuart Henry-Rene Romero - Pediatric Transplantation - 2007
3. Neonatal Hemochromatosis: A Congenital Alloimmune Hepatitis - Peter Whitington - Seminars in Liver Disease - 2007
4. Neonatal hemochromatosis: The importance of early recognition of liver failure
Pankaj Vohra-Cindy Haller-Sukru Emre-Margret Magid-Ian Holzman-Ming Ye-Elizaveta Iofel-Benjamin Shneider - The Journal of Pediatrics - 2000
5. Neonatal Liver Cirrhosis Without Iron Overload Caused by Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease.
Debray-François Guillaume de Halleux- Virginie Guidi-Ornella Detrembleur-Nancy Gaillez-Stéphanie Rausin-Léon Goyens-Philippe Pan-Xiaomin Whitington Peter-Pediatrics-2012
6. Neonatal Liver Failure and Congenital Cirrhosis due to Gestational Alloimmune Liver Disease: A Case Report and Literature Review
Oscar Roos Mariano da Rocha Carolina-Renata Rostirola Guedes- Carlos Oscar Kieling- Marina Rossato Adami- Carlos Thadeu Schmidt Cerski- Sandra Maria Conçalvez Vieria - Hindawi - 2017
Image: (A) MRI liver showing normal appearance without evidence of hemochromatosis (B) MRI brain showing no evidence of iron deposition within the brain parenchyma (C) MRV head showing right transverse and sigmoid venous sinus thrombosis
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal